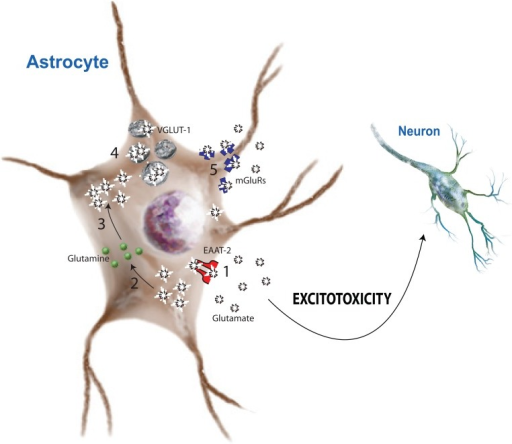
Glutamate Excitotoxicity in the Brain
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter found throughout the brain in small concentrations, and is directly related to the ability to learn, attend, and cognitively function. Glutamate levels are physiologically held in check by conversion to gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA), an inhibitory neurotransmitter also found throughout the brain. The conversion of Glutamate to GABA occurs via the enzyme Glutamic Acid Decarbolxylase, which in a “normal” brain, keep Glutamate from becoming too high, and GABA from becoming too low.
Interestingly, the rubella virus found in the MMR vaccine, interferes with Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase proper functioning, which is why some children have adverse neurological symptoms following the MMR vaccine. This is probably particularly true in patients who are born with Lyme Disease and/or coinfections.
In patients with neurological Lyme Disease or PANDAS, we frequently see behaviors including:
- Insomnia
- Agitation
- Abnormal eye movement
- Disruptive behavior
These behaviors are suggestive of elevated levels of Glutamate in the brain. Additionally, elevated Glutamate depletes the endogenous Glutathione in the body, a critical antioxidant.
Identifying and correcting the Glutamate/GABA imbalance in the brain can be done by using an organic acid urine test, and then natural substances can be introduced to correct the imbalance. This may be some of the problems seen in neurological Lyme Disease.
For furthermore information about this phenomenon, please talk to Dr. Marra and she can order the appropriate tests to identify the underlying biochemical dysfunction.